Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnusIt is one of the largest, fastest and most valuable commercial fish species in the world. Its impressive speed, powerful musculature, and ability to travel thousands of kilometers in search of food make it the true king of the oceans.
It is an important component of marine ecosystems, but overfishing threatens the population of this fish. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the biology, behavior, habitat, threats, and conservation measures of this amazing species.

1. General characteristics of Atlantic bluefin tuna
🔬 Scientific classification:
✔ The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
✔ Type: Chordal (Chordata)
✔ Class: Lucheperi pisces (Actinopterygii)
✔ Row: Perch-like (Perciformes)
✔ Family: Mackerel products (Scombridae)
✔ Gender: Tuna fish (Thunnus)
✔ View: Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus)
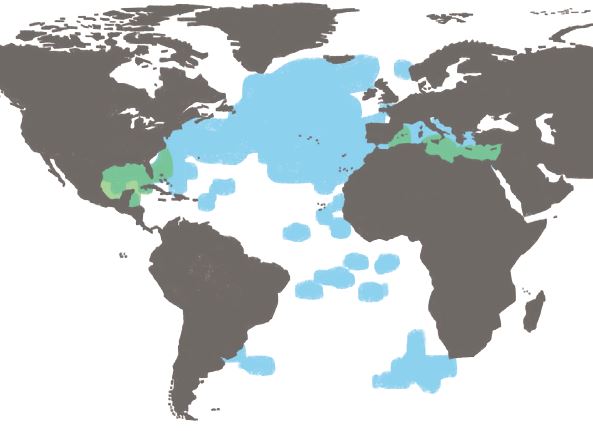
📍 Area:
* Atlantic Ocean (from North America to Europe and Africa)
* Mediterranean Sea (main spawning area)
* Can enter the Gulf of Mexico and the North Sea
📏 Sizes:
* Length: up to 4.6 m
* Weight: up to 680 kg
📌 Interesting!
The largest recorded specimen weighed 679 kg!
🏃 Speed:
* Up to 75 km / h
🌡 Temperature range:
* From 3°C to 30°C
2. Appearance and anatomy
🔹 Body:
✔ Streamlined, torpedo-shaped-perfectly adapted for fast swimming
✔ Large size and massive musculature
🔹 Color scheme:
✔ Back-dark blue, almost black
✔ Belly-silver-white
✔ On the sides – a characteristic metallic sheen
🔹 Fins:
✔ Pectoral fins-small
✔ Dorsal fin-high and sickle-shaped
✔ Tail fin-in the shape of a crescent (allows you to develop high speed)
📌 Unique Feature:
Atlantic bluefin tuna can regulate your body temperaturewhich allows it to survive in cold waters.
3. Lifestyle and behavior
🛶 Migrations:
✔ Travel thousands of kilometers between feeding and spawning sites
✔ Main migration routes-between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea
📌 Interesting!
Tuna can cross the Atlantic Ocean in just 50 days!
🐟 Social structure:
✔ Swims in large flocks
✔ Packs can include different types of tuna
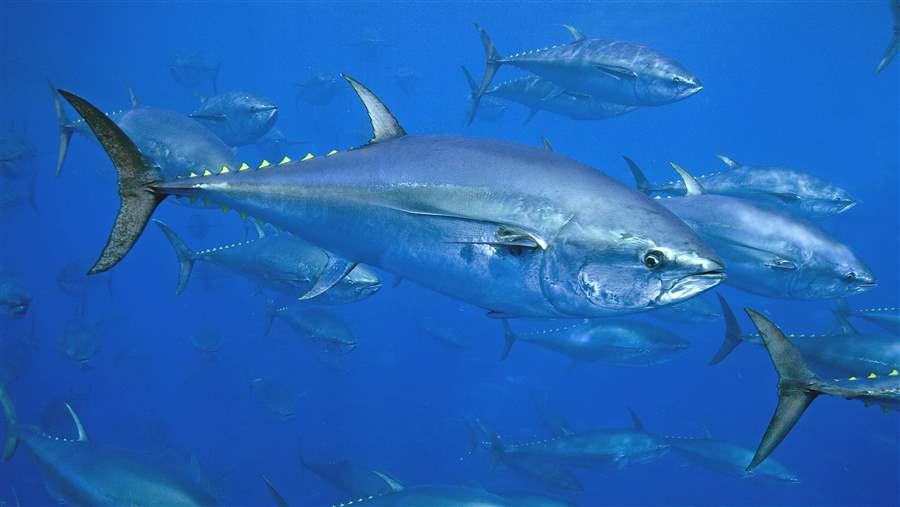

4. Feeding and predatory behavior
Atlantic bluefin tuna – active predator with excellent eyesight and speed.
🍽 Basic diet:
✔ Herring (Clupeidae)
✔ Sardines (Sardina pilchardus)
✔ Mackerel (Scomber scombrus)
✔ Squid
✔ Crayfish
📌 Interesting!
This type of tuna has one of the highest food conversion rates - it grows rapidly due to the large amount of fish consumed.
5. reproduction and life cycle
🌊 Spawning grounds:
✔ Mediterranean Sea
✔ Gulf of Mexico
🕑 Spawning time:
✔ May-July
🐟 Features of reproduction:
✔ A single female can lay up to 30 million eggs
Larvae grow rapidly and become predators in the first year of life
📌 Interesting!
Young tuna are growing at a rapid rate 10 kg per year!

6. industrial catch and threats
📉 Population decline:
✔ Overfishing has reduced the population by 85% in the last 50 years
✔ High demand in Japan for sushi and sashimi caused an intensive catch
⚖ Security measures:
✔ Catch limit
✔ Marine reserves
✔ Artificial breeding programs
📌 Interesting!
In 2013, one tuna at an auction in Japan was sold for 1.76 million dollars!
7. Role in the marine ecosystem
🌊 Top-level Predator:
✔ Controls small fish populations
✔ Important for the health of marine ecosystems
⚠ Impact on tuna populations:
✔ Overfishing can change the balance of the food chain
✔ Protecting the species is the key to preserving ocean ecosystems
8. Interesting facts about Atlantic Bluefin tuna
✔ One of the few fish species that can support body temperature is higher than water temperature
✔ The fastest tuna-develops speeds up to 75 km / h
✔ Swims long distances non-stop
✔ Can change your body colorto communicate with other people
Conclusion
Atlantic bluefin tuna is a true ocean giant that is revered for its speed, strength and taste. Its role in marine ecosystems is crucial, and overfishing poses a serious threat to this amazing species.
Thanks to international protection programs, catch restrictions and artificial breeding, there is hope for preserving the population of this unique predator for future generations.
