The sheepdog (Ovibos moschatus) is a large member of the bovine family that lives in the cold Arctic and subarctic regions of North America and Greenland. This amazing mammal is known for its ability to withstand the harsh conditions in which it lives and at the same time maintain a high level of activity in the cold. Bighorn sheep have numerous adaptations that allow them to survive in extreme conditions. In addition, their impressive horns and thick fur make them one of the most memorable animals of the tundra.

Classification and scientific name
• Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
- Type: Chordate
- Class: Mammalia
- Order: Artiodactyla
- Family: Bovidae
- Re: Ovibos
• View: Ovibos moschatus
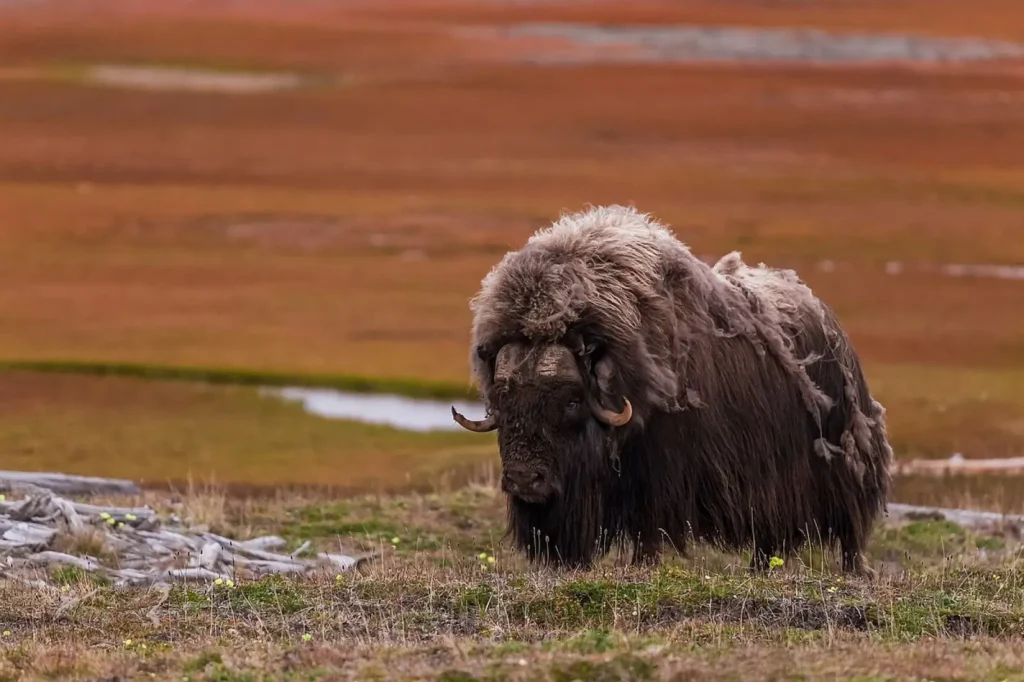
Appearance
📏 Sizes
A sheep is a huge animal. Adult males can weigh up to 450 kg, and females are slightly smaller - up to 250 kg. Their body length can reach 2.5 meters, and height at the shoulders is about 1.3 meters. Their impressive size makes them noticeable even in the harshest conditions.
🎨 Color scheme
The body of a sheepdog is covered with thick, dense fur that is dark brown or blackish in color. They have very short but dense fur, which insulates perfectly from the cold. The fur is shorter on the face and legs, but even here the animals have good thermal insulation. They have a pronounced feather coating, which, together with their massive horns, gives them a spectacular appearance.
🦸♂️ Features of the structure
Musk oxen have very powerful legs that allow them to move across tundra and ice. Their thick hide helps to keep them warm, and a deep layer of blubber gives them extra insulation, allowing them to withstand extreme cold down to -50°C. Their large male horns are used in battles for territory and females.
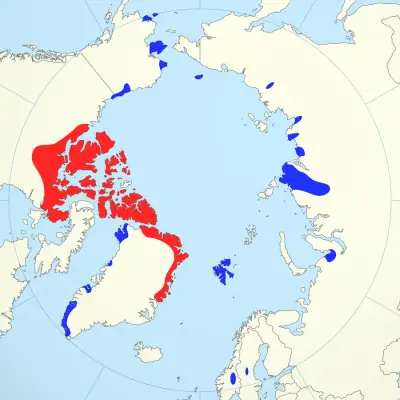
Range and habitat
🌍 Spread
Musk oxen live in the Arctic and subarctic regions, mainly in Canada, Greenland, and the northern regions of Alaska. They are often found on open plains where they graze on grass meadows and mossy tundras. Bighorn sheep are adapted to living in low temperatures and strong winds.
🌿 Place of residence
Bighorn sheep are found in areas with extensive snow cover and ice fields. They like open spaces where they can gather in large groups to protect themselves from predators and unfavorable weather conditions. Winter is a time of maximum difficulty for them, when they have to survive on a minimum of food, covering long distances in search of food.
Food
🌾 Ration
Bighorn sheep are herbivores, and their diet consists mainly of a variety of vegetation, including mosses, lichens, grasses, and shrubs. They also consume young shoots of trees, particularly birch and aspen. In harsh winters, it is difficult for them to find food, so they are dependent on nutritious plants that remain under the snow cover.
🌱 Water consumption
These animals do not need a lot of water, as they are able to obtain moisture from snow and from the plant foods they consume. They usually find water in rivers and lakes near their habitats.
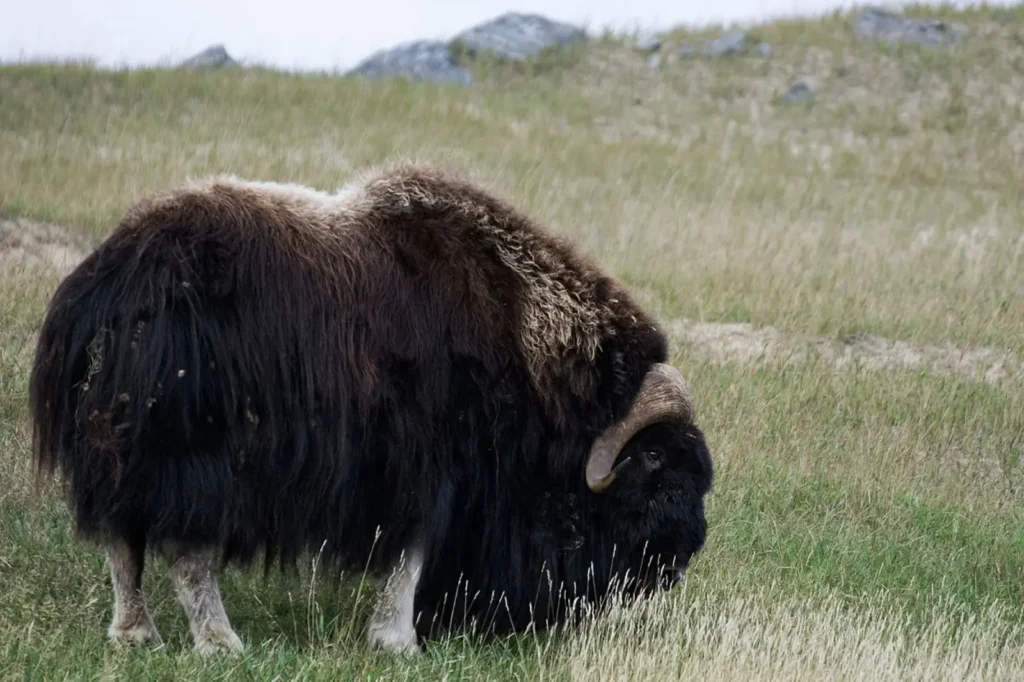

Behavior and lifestyle
🌬 Activity
Bighorn sheep are usually active during the day and night. They move in groups of 5 to 15 individuals, but can form larger flocks. Their behavior is closely related to finding food and protecting themselves from the cold. In severe winter winds and frosts, they can move long distances in search of food. In the summer, their activity decreases and they spend more time resting.
🐾 Social structure
Sheep live in herds with a clear social hierarchy. Males often fight among themselves for leadership and the right to access females. These fights are often accompanied by brutal clashes of their horns.
Reproduction
🍼 The process of reproduction
Bighorn sheep breed once a year, usually in the fall or winter. Pregnancy lasts about 8 months and usually one cub is born. A litter is born in the fall, before the harsh winter sets in. The cubs are born quite large and can quickly follow their mother.
👶 Development of offspring
The cubs grow quite quickly, and in a few weeks they can walk and graze with the adults. From the moment of birth, cubs start receiving milk from their mother, but from the first month their diet is supplemented with plant foods. At the age of 1 year, young animals become independent, although they can remain part of the herd.
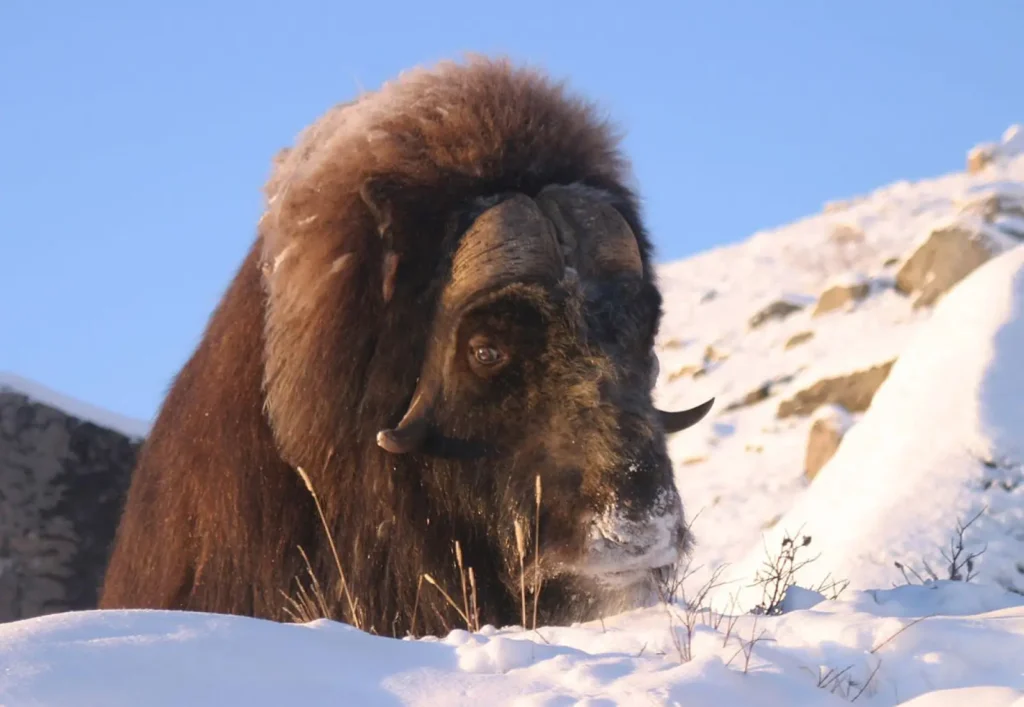

Threats and protected status
⚠️ Threats
The main threats to bighorn sheep are climate change, which leads to a reduction in their natural habitat, as well as hunting and poaching. The removal of bighorn sheep from their natural habitat to zoos or farms sometimes poses an additional threat to their survival.
🛡 Protection status
The bighorn sheep is an internationally protected species, and its population is being preserved through various conservation programs and reserves. The species is considered vulnerable due to declining numbers as a result of habitat loss and climate change.
Interesting facts
✔️ Sheep can withstand extreme temperatures down to -50°C thanks to their thick fur and subcutaneous fat layer.
✔️ Their large horns are used to fight for females and territory.
✔️ Bighorn sheep are able to travel great distances in search of food, often leaving deep tracks in the snow.
✔️ It is known that musk oxen can travel up to 100 kilometers in search of food, making them one of the most mobile mammals in the Arctic.
Conclusion
The musk ox is an incredibly strong and hardy animal that is an important part of Arctic ecosystems. Thanks to its adaptations to living in cold and extreme weather conditions, this species remains one of the most unique animals in the northern regions. With their social structure and powerful size, musk oxen continue to amaze researchers and are an important symbol of survival in the harsh environment.