Cotophreda striped (Bassariscus astutus), also known as ring-tailed cat, Western civilization or minor pantheris a small carnivorous mammal from the raccoon family (Procyonidae).
Despite its name, this animal is neither a cat nor a ferret, but is most closely related to raccoons. It has a slender body structure, large eyes, and a characteristic long tail with black and white rings.
This nocturnal animal is known for its gymnastic agility and the ability to climb rocks, trees, and even vertical surfaces.
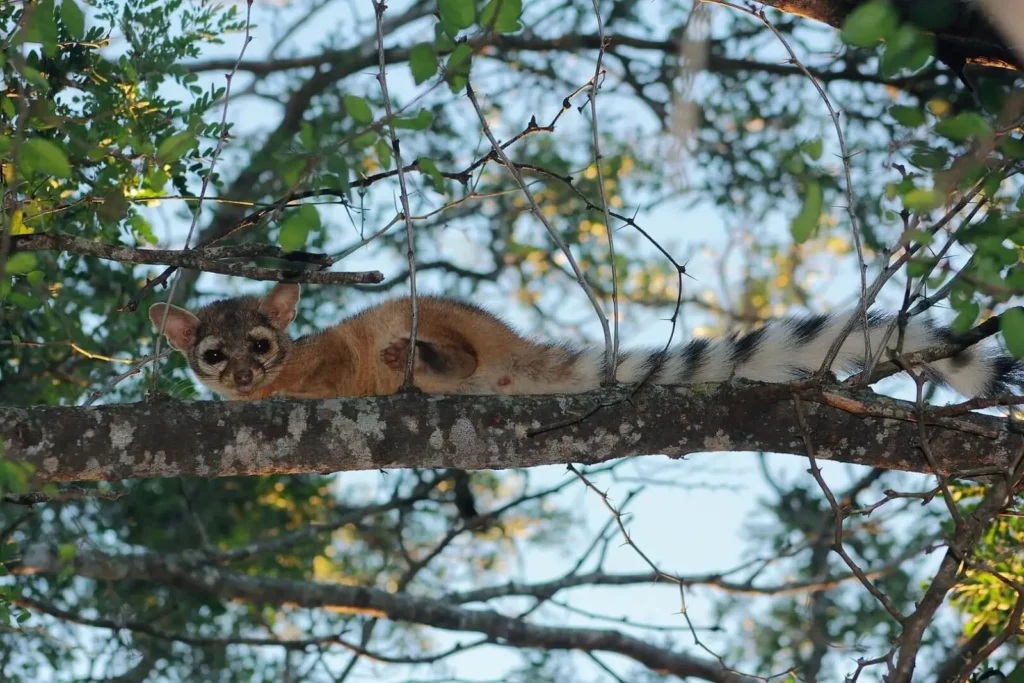

Classification
• The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
• Type: Chordal (Chordata)
• Class: Mammals (Mammalia)
• Row: Predatory (Carnivora)
• Family: Raccoon (Procyonidae)
• Gender: Bassarisk (Bassariscus)
• View: Cotophreda striped (Bassariscus astutus)
📌 The closest relative is the Central American bassariscus (Bassariscus sumichrasti), which lives in Central America.
Appearance
🟤 Dimensions and weight
• Body length: 30-42 cm
• Length of the tail: 31-44 cm
• Weight: 0.8-1.5 kg
🟤 Color scheme
- Main coloration brownish-beige or grayish
- Belly light or white
- The main feature is fluffy tail with black and white rings
🟤 Features of the structure
• Slender and flexible bodyadapted for climbing
• Big eyes with good night vision
• Sharp claws and clingy paws
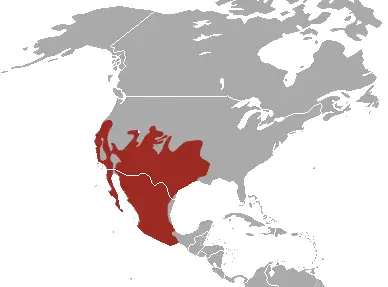
Habitat range
The striped cotophreda lives in North America, separately:
• Southern USA (California, Arizona, Texas, Utah, New Mexico)
• Mexico
She can be found in rocky canyons, deserts, forests, mountains and even near human settlements.
Lifestyle and behavior
✅ Nighttime activity
Kotofredka goes hunting after sunset, using her keen eyesight and hearing to find prey.
✅ Solo lifestyle
These animals lead solitary lifestyleexcept for the breeding season.
✅ Acrobatic skills
- Skills. jump 1.5 meters in height
- Maybe move through narrow branches and rocks
- Uses the tail to balancing
✅ Absence of aggression
Cotophreda avoids conflicts and usually runs away from predators.
Food
🦗 The opportunistic predator
Kotofredka eats whatever she can find:
• Insects (beetles, crickets)
• Rodents (mice, squirrels)
• Lizards and birds
• Fruits and berries
• With bird eggs
In the fall, they are especially active in eating fruits, berries and nutsin preparation for the cold season.
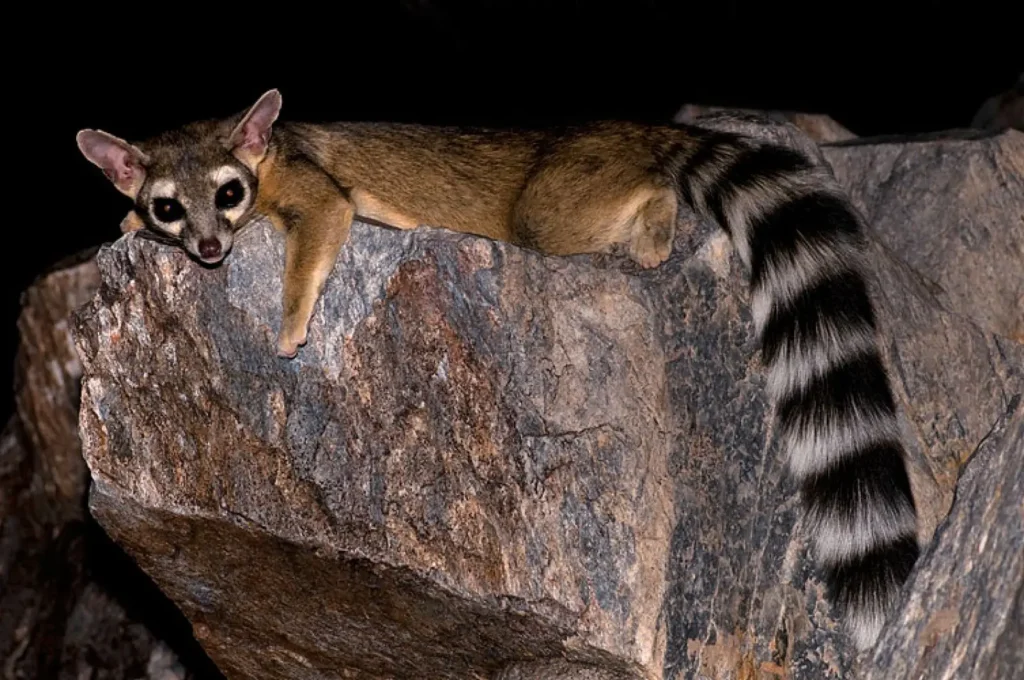

Reproduction
🍼 Mating season: spring (March-May)
* Pregnancy continues 50-60 days
* Born 2-4 kids
- A mother takes care of her cubs about three monthsafter which they become independent
Young bassaris are very playful and quickly learn to climb and hunt.
Natural enemies
Among the main predators that can hunt cottontails:
- 🦅 Great owls (e.g., an owl)
- 🐍 Snakes
- 🦊 Foxes
- 🐆 Lynx
However, due to their agility, they often resort to escape or disguise.
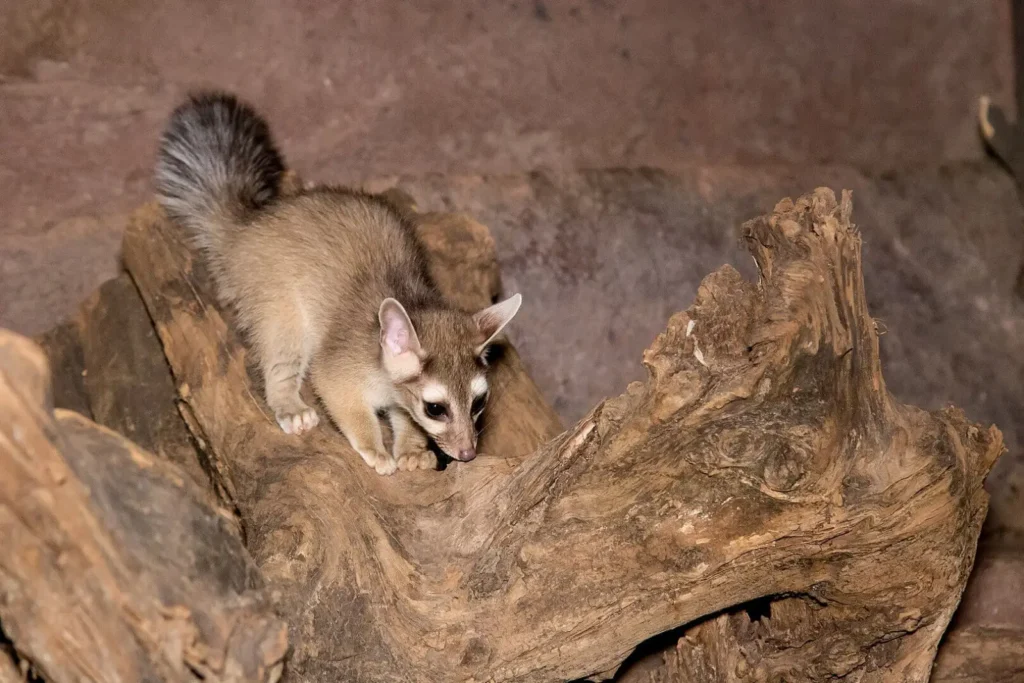

Population status and protection
✅ Not endangered
Cotophreda striped has stable population and adapts to changes in the environment.
🏡 Lives near people
Sometimes these animals settle near human dwellings and can enter garbage bins in search of food.
🚫 Threats
- Destruction of the natural environment
- Deaths on the roads
- Hunting for skins
However, in many regions, this species protected by law.
Interesting facts
🔸 It is the official mammal of the state of Arizona (USA)
🔸 Maybe rotate 180 degrees around the axis, which helps to climb branches
🔸 Almost odorlesswhich distinguishes it from other raccoons.
🔸 Life expectancy in the wild - up to 7 years, in captivity - up to 15 years
Conclusion
Cotophreda striped (Bassariscus astutus) is an amazing nocturnal animalwho has outstanding gymnastic skills. Thanks to her agility, intelligence and adaptabilityIt easily survives in the wild and even adapts to environmental changes.
This view remains one of the least studied among raccoonsbut its charming appearance and curious behavior make it a real treasure of North American fauna.
📌 Would you like to see this unique animal in the wild? 😃
