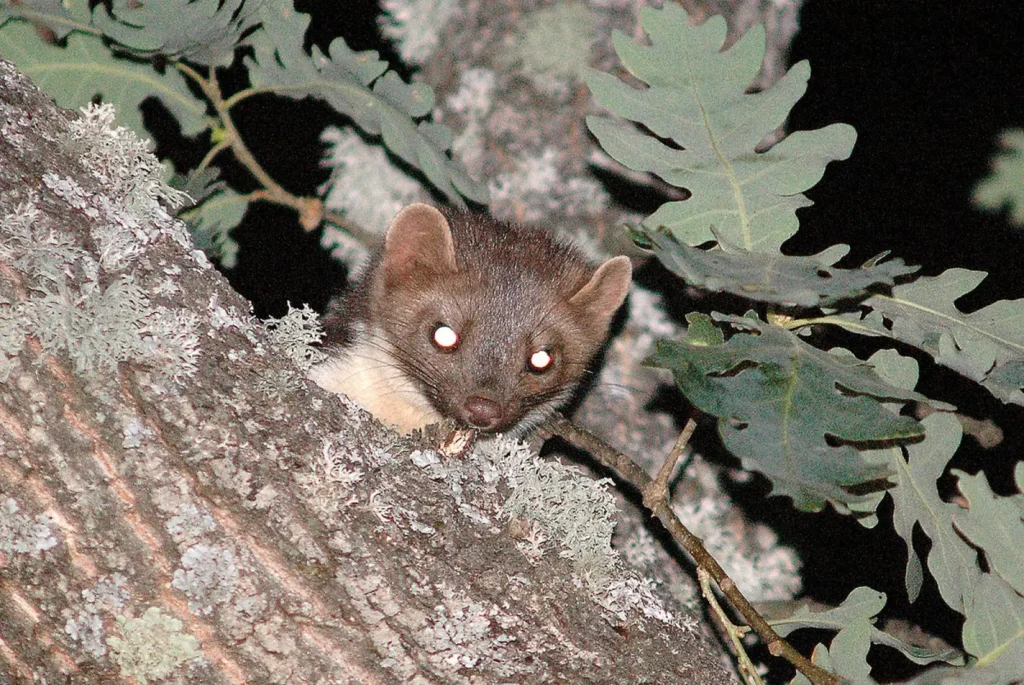
Stone marten (Tuesdays foina) – a carnivorous mammal of the marten family (Mustelidae), known for its agility, endurance, and ability to adapt to different environments. It is found in Europe, Asia, and North Africa and is the closest relative of the pine marten (Tuesday TuesdayThe stone marten is known for often settling near human settlements, hence the name - it often lives among stone buildings, ruins, and rocks.
This animal plays an important role in ecosystems by controlling the numbers of rodents and other small animals. However, its activities can cause problems for humans, as it has a habit of climbing into cars and buildings.

Classification and scientific name
• The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
• Type: Chordal (Chordata)
• Class: Mammals (Mammalia)
• Row: Predatory animals (Carnivora)
• Family: Martens (Mustelidae)
• Gender: Martens (Tuesdays)
• View: Stone marten (Tuesdays foina)
Physical characteristics
Dimensions and weight
📌 Body length: 40–54 cm
📌 Tail length: 22–30 cm
📌 Weight: 1–2.5 kg
The rock marten is slightly smaller than the wood marten, but has a similar build.
Color and fur
✔ Main coat color: gray-brown or brown
✔ Throat mark: a white or cream patch that bifurcates on the chest
✔ Tail: fluffy, dark brown
The main difference between the rock marten and the forest marten is the color of the breast spot: in the rock marten it is white, and in the forest marten it is yellowish.
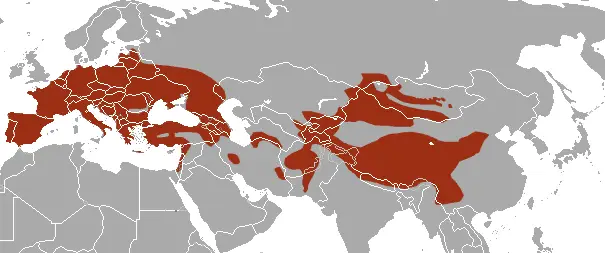
Range and habitat
🔵 Spread
The stone marten lives in different regions:
• Europe – from Spain to Ukraine
• Asia – Turkey, Caucasus, Iran, Mongolia, China
• North Africa - Morocco, Algeria
🔴 Living environment
✔ Mountainous areas and cliffs
✔ Forests, forest-steppes, plains
✔ Agricultural land
✔ Suburbs and urban areas
The stone marten easily adapts to life near people, often settling in attics, in storerooms, and even in car engines.
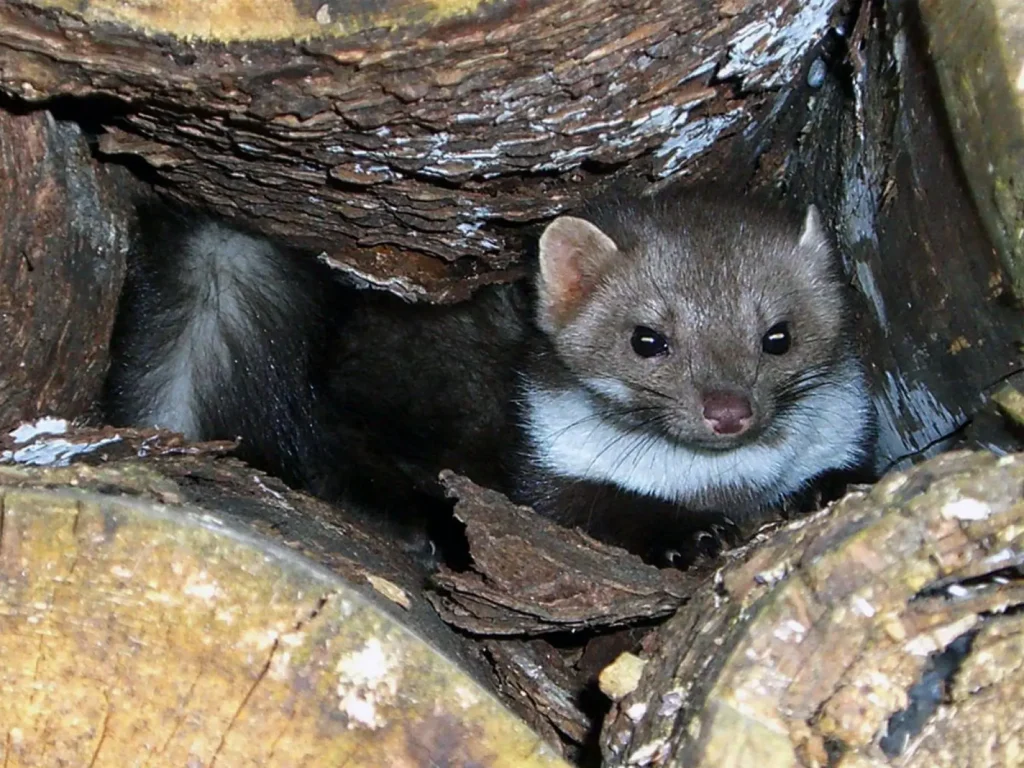
Lifestyle and behavior
🌟 Social structure
✅ Solo lifestyle (except during the marriage period)
✅ Males and females occupy separate territories
✅ Marked by territoriality
🌟 Activity time
✅ Mostly nocturnal
✅ Hunts and searches for food in the dark
✅ Spends the day in hiding places: hollows, crevices, under the roofs of houses
🌟 Main behavioral features
✔ Excellent cragsman
✔ Very careful, easily avoids danger
✔ Makes long journeys in search of food

Food and hunting
🍖 Omnivory is the key to success
The stone marten is opportunistic predator, who eats everything he can find.
✅ Typical food sources:
✔ Rodents (mice, voles, rabbits)
✔ Birds and their eggs
✔ Insects, amphibians
✔ Fruits, berries
✔ Distance
💡 Methods of obtaining food
• Climbs trees, searching for nests
• Hunts from ambush, using speed and jumping ability
• Uses a keen sense of smell to find food
Reproduction and life cycle
❤️ Mating season: June – August
❤️ Pregnancy: 7–9 months (due to latent implantation)
❤️ Number of children: 2–4 (sometimes up to 7)
❤️ Puberty: at 15–27 months
👶 Babies are born blind, helpless
👩👧 The mother feeds them with milk for 6–7 weeks.
👨👩👦 By autumn, the young become independent.
🧬 Life span:
• In the wild – 8–10 years
• In captivity – under 18 years old
Natural enemies and threats
🔴 Birds of prey and animals
✔ Wolves, foxes
✔ Eagles, owls
🔴 Threats from humans
✔ Hunting for fur
✔ Poisoning and traps
✔ Destruction of the natural environment

Conservation status and conservation measures
🟢 Security status:
🔹 It is considered a species that is not in danger of extinction.
🔹 In some regions, its numbers are declining due to human influence.
🟢 Security measures:
✔ Protection of forests and natural areas
✔ Hunting restrictions
✔ Population studies
The rock marten and man
❗ Problems caused by martens near people
• Gets into houses, destroys roof insulation
• Chews through wires in cars
• Arranges hiding places in basements, sheds
💡 How to scare away a marten?
• Use ultrasonic repellers
• Close ventilation holes in buildings
• Treat the car with special products
Conclusion
The stone marten is smart, cunning and hardy animal, which plays an important role in nature by controlling the number of rodents. At the same time, it can cause inconvenience to people by settling in houses and cars. Despite certain threats, this species has a high chance of survival due to its ability to adapt to different conditions.