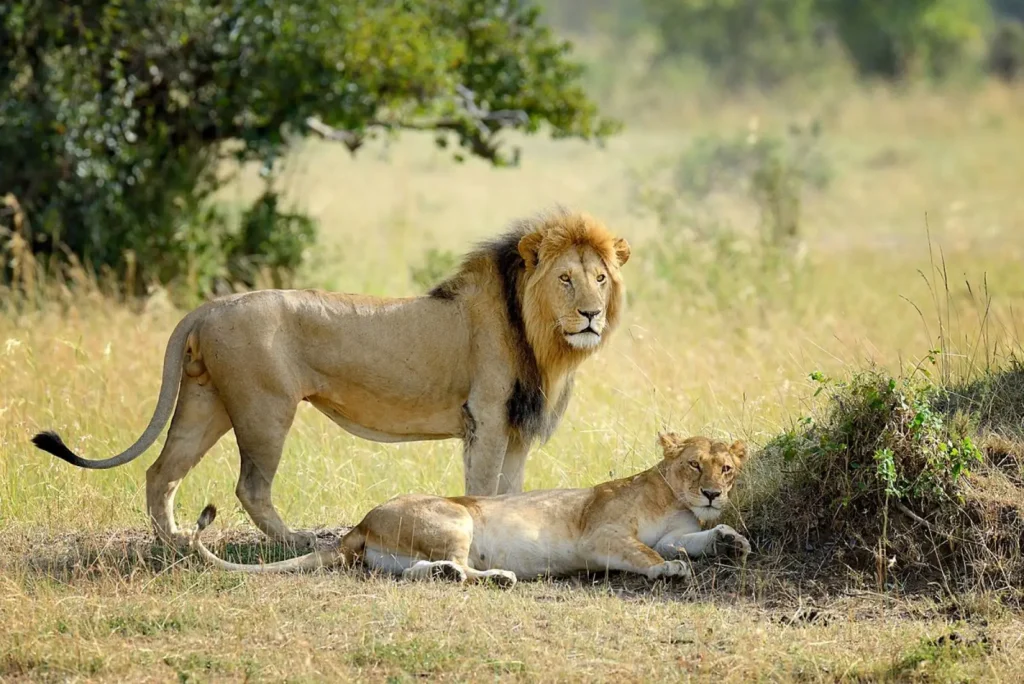
Leo (Panthera leo) is one of the largest predators on our planet, which for centuries personified strength, courage and power. Its powerful roar can be heard at a distance of up to 8 km, and the male with a luxurious mane is a symbol of the wildlife of Africa. However, lions are not only symbols of power, but also complex social animals that live in harmonious prides.
They once inhabited almost all of Eurasia and North America, but today they remain only in Africa and part of India. Their numbers are decreasing due to loss of natural territories and poaching. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the biology of lions, their behavior, habitat, threats and efforts to preserve them.

Scientific classification
✔ The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
✔ Type: Chordal (Chordata)
✔ Class: Mammals (Mammalia)
✔ Row: Predatory animals (Carnivora)
✔ Family: Feline (Felidae)
✔ Gender: Panthera
✔ View: Leo (Panthera leo)
Appearance and features
✔ Sizes:
• Males: 170–250 cm in length (excluding tail), weight 150–250 kg
• Females: 140–180 cm in length, weight 100–180 kg
✔ Tail: 60-100 cm
✔ Shoulder height: 90-120 cm
✔ Color scheme: from light yellow to dark brown
✔ Mane: only found in males, its color varies from golden to black
The mane not only makes lions more attractive, but also protects their neck and head during fights. The darker the mane, the higher the testosterone levels and the stronger the male.
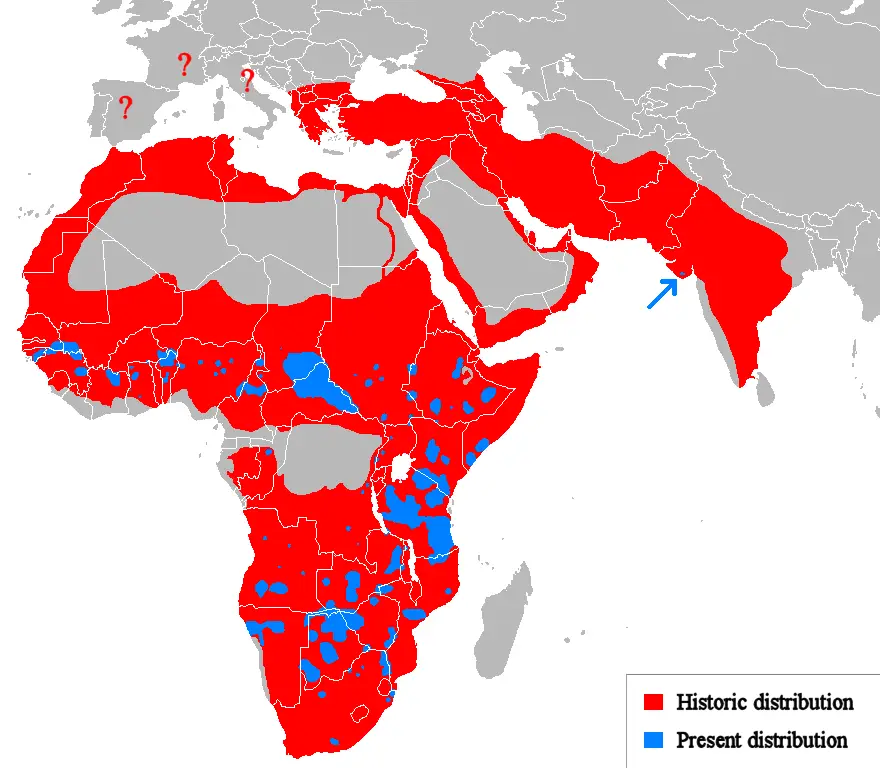
Habitat and distribution
🌍 Where do lions live?
✔ Africa: main range in savannas south of the Sahara (Tanzania, Kenya, Botswana, South Africa, Namibia)
✔ India: small population in Gir National Park (Gujarat state)
🦁 Once upon a time, lions lived:
✔ In Europe, the Middle East, India and even America
✔ In ancient Rome, lions were used in gladiatorial combat
The species' range has now been reduced by over 80% due to human activity.
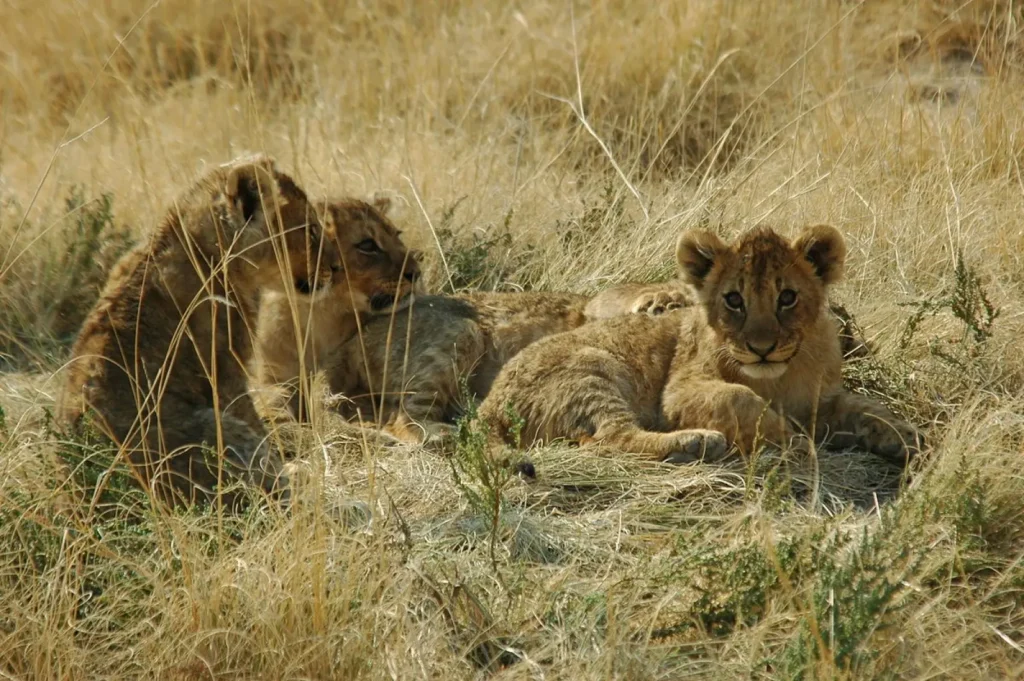
Social structure: pride – the heart of the lion community
Lions are the only big cats that live in groups.
🔹 Pride is a family structure that includes:
✔ 3–12 females (they are relatives)
✔ 1–3 males (usually brothers or close relatives)
✔ 10–15 cubs

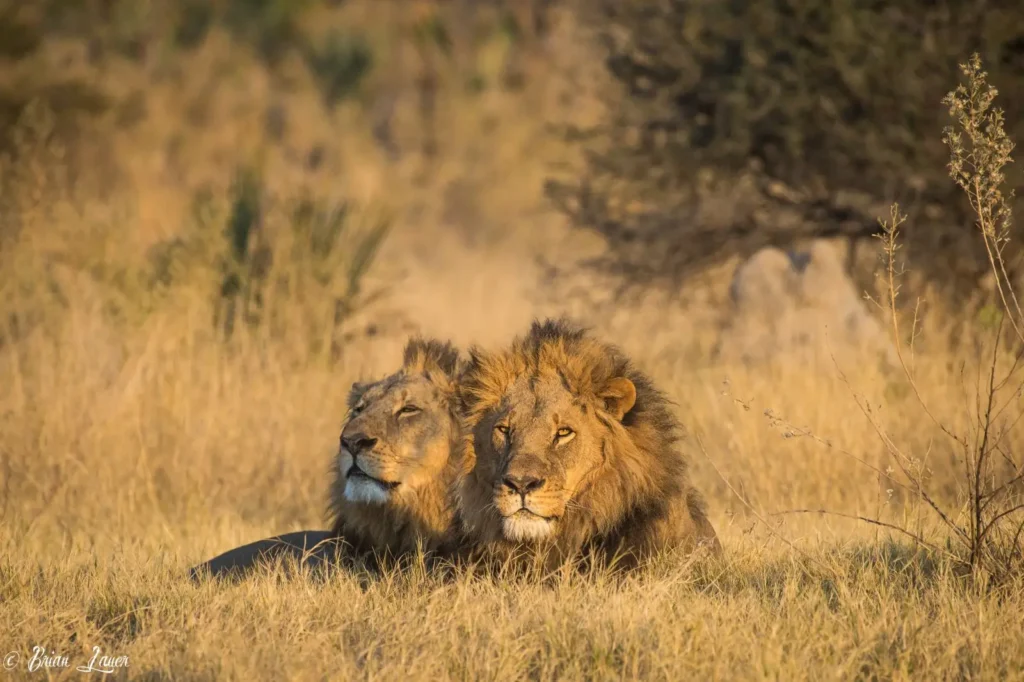
🔹 The role of males:
✔ Protect the pride from other lions
✔ Mark territory with urine and roaring
✔ They hunt less often, but can take prey from females
🔹 The role of females:
✔ Hunt and provide food for the pride
✔ They take care of their young, even if they are not theirs
Males rarely remain in the same pride for longer than 3–5 years, after which they are displaced by younger competitors.
Hunting and dieting
Lions are at the top of the food chain, and although they are often considered lazy, they are extremely efficient predators.
🍖 What do lions eat?
✔ Antelopes, zebras, buffaloes, giraffes
✔ Young elephants and rhinos (very rare)
✔ Hippos (during dry periods)
✔ Can take prey from hyenas and leopards
💨 Hunting tactics:
✔ Lions hunt at night or at dawn
✔ Females attack in packs, surrounding their prey
✔ Males only join for large prey
Cooperative hunting allows lions to attack animals much larger than them.
Reproduction and young
🦁 Interesting facts about lion reproduction:
✔ Males mate with multiple females
✔ Pregnancy lasts 110 days
✔ 2–4 lion cubs are born
✔ Females feed not only their own but also other lion cubs
✔ Cubs live in the den for 6 weeks and then join the pride
Only 20–30% of lion cubs survive to adulthood due to predator attacks, disease, or killing by new males in the pride.

The voice of lions: a roar that can be heard 8 km away
🦁 Lions roar to:
✔ Mark the territory
✔ Notify Pride of your location
✔ Warn strangers of danger
Males roar louder than females, and their roar can be heard up to 8 km away!
Main threats to lions
🔴 Why are lion populations declining?
✔ Habitat loss – through the expansion of agriculture
✔ Conflicts with people – farmers kill lions to protect livestock
✔ Poaching – bones and body parts of lions are used in traditional medicine
✔ Climate change – reduce the amount of prey
100 years ago, there were over 200,000 lions in Africa, and today there are no more than 20,000 left.
Protection and preservation
🔵 What are they doing to protect lions?
✔ Nature reserves and national parks (Serengeti, Kruger)
✔ Anti-phishing programs – fight against poaching
✔ Educational campaigns – reducing conflicts with farmers
✔ Reintroduction – returning lions to the wild
Without these measures, lions could be threatened with extinction as early as the 21st century.
Interesting facts about lions
🦁 Lions sleep up to 20 hours a day
🦁 The lion is the only big cat that lives in packs
🦁 In ancient Egypt, lions symbolized military power
🦁 Females hunt more often, but males eat first
Conclusion
Lions are not only a symbol of wildlife, but also key predators of African ecosystems. Their conservation is a challenge for humanity that requires active action.
🦁 Have you ever seen lions in the wild or in a zoo? Share your impressions in the comments!