Gray wolf (Wolf dog) is one of the most famous and mysterious predators on the planet. Its image is often surrounded by myths, legends and fear, but these animals play an extremely important role in natural ecosystems.
Being the largest member of the canine family (Canidae), wolves have a complex social structure, a high level of intelligence, and a developed communication system. Despite persecution by humans, they have been able to maintain their populations in many parts of the Earth.
In this article, we will look at the biological characteristics, habitat, behavior, diet, threats, and interactions of the gray wolf with humans.
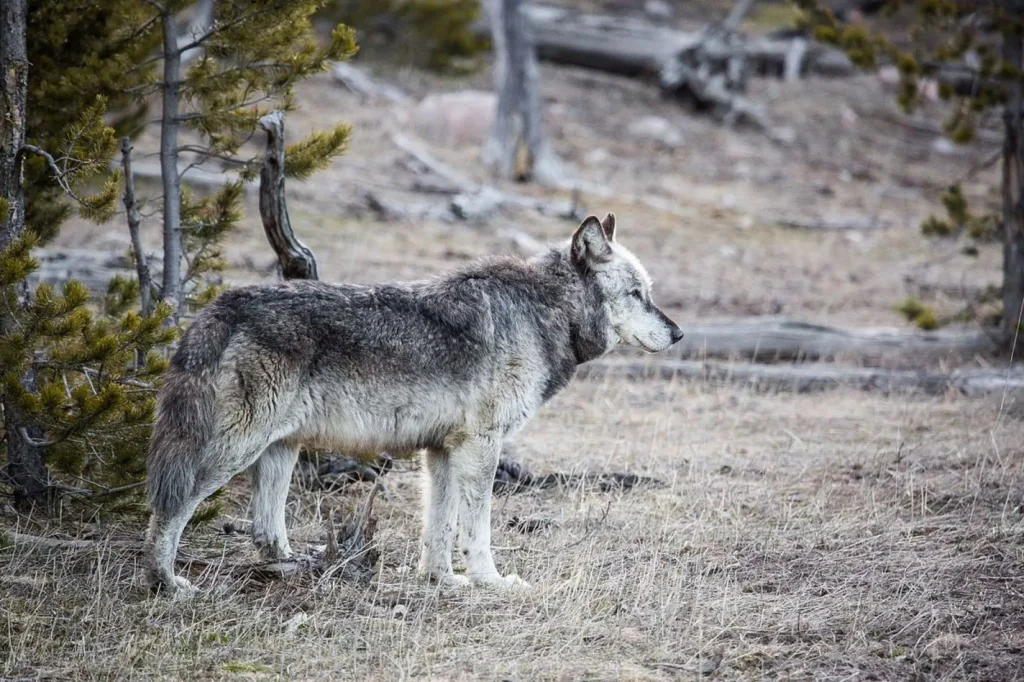

Scientific classification
✔ The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
✔ Type: Chordal (Chordata)
✔ Class: Mammals (Mammalia)
✔ Row: Predatory animals (Carnivora)
✔ Family: Canines (Canidae)
✔ Gender: Canis
✔ View: Wolf dog
🔎 Interesting! The wolf has over 30 subspecies, including such well-known representatives as the Eurasian wolf (Wolf dog wolf), American wolf (Western wolf dog) and Arctic wolf (Canis lupus arctos).
Appearance and features
✔ Sizes:
• Body length: 100–160 cm
• Height at the withers: 65–90 cm
• Weight: 25–80 kg (males are usually larger than females)
✔ Color scheme:
• Fur color varies from light gray to black
• Some subspecies have reddish and white coloring
✔ Body type:
• Long legs and a flexible body adapted for fast movement
• Sharp teeth and powerful jaws that can develop pressure of up to 400 kg/cm²
• The fur has a thick undercoat that helps it survive the cold
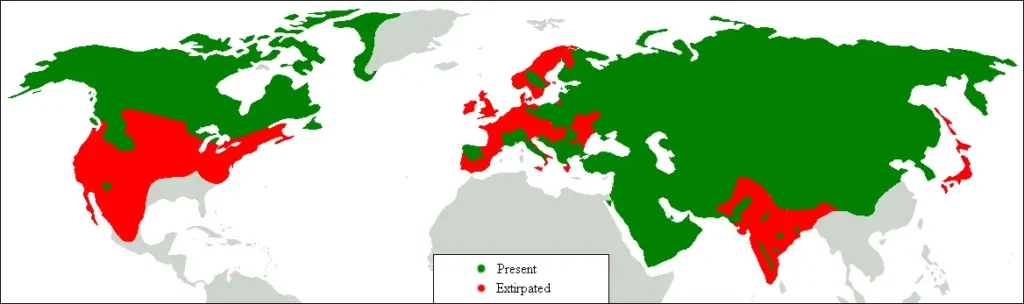
Habitat and distribution
🌍 Where do gray wolves live?
✔ Forests, tundra, steppes, mountains, taiga - they are adapted to life in different conditions
✔ Main area: North America, Europe, Asia
🔴 Threats to the habitat:
✔ Deforestation and reduction of natural areas
✔ Persecution by people due to attacks on livestock
✔ Extinction of the species they feed on
Social behavior and flocks
🐺 How do wolves live?
✔ They form packs (5–15 individuals) in which a strict hierarchy prevails
✔ The pack has alpha pair – the main male and female that reproduce
✔ Each member fulfills their role: hunters, guards, nannies for wolf cubs
🔹 Territorial behavior:
✔ Each pack has its own territory (from 50 to 1000 km²)
✔ They mark the boundaries of their territory with smells and howls
🔹 Communication:
✔ Howling – signaling the flock about its presence
✔ Gestures, postures, and sounds convey emotional state

Diet and hunting method
🍖 What do wolves eat?
✔ Main food – ungulates: deer, elk, roe deer, wild boars
✔ Also feed on small mammals, birds, and fish
✔ In times of famine, they may consume carrion
🔎 How do they hunt?
✔ Hunting takes place in packs
✔ Use the strategy of driving prey into a trap
✔ Able to run up to 60 km per day in search of food
Reproduction and offspring
🐺 How are wolf cubs born?
✔ Pregnancy lasts 60–65 days
✔ 4–7 cubs are born
✔ They are blind and helpless, the female takes care of them in the den
🔹 Raising wolf cubs:
✔ The entire pack participates in caring for the young
✔ Wolf cubs begin to leave the den at the age of 3 weeks
✔ They learn hunting skills from adults

Human interaction
🔴 Conflicts:
✔ Wolves attack livestock
✔ Hunting and myths about wolves caused their mass extinction
✔ People were often afraid of wolves, although attacks on humans are rare
🛡 Protection and preservation:
✔ In many countries, wolves are protected
✔ Their role in nature is important – they regulate the population of ungulates
✔ Conservation programs help restore wolf populations
📈 Population:
✔ In the 20th century, many wolf populations were destroyed
✔ Nowadays, the number of wolves is stabilizing due to protection
Interesting facts about wolves
🐺 A wolf's howl can be heard up to 10 km away
🐺 Wolves can run at speeds up to 60 km/h
🐺 They have an extremely keen sense of smell – 100 times better than a human’s
🐺 Wolves form strong social bonds and mourn the death of pack members
Conclusion
The gray wolf is an amazing predator that plays a key role in natural ecosystems. Its complex social structure, strategic thinking, and endurance make it one of the most successful hunters in the wild.
Despite centuries of persecution, wolves continue to exist and adapt to change, proving their strength and importance to the balance of nature.
🐺 Do you think wolves should be fully protected, or should their numbers be regulated? Share your thoughts!