Among the inhabitants of the northern seas, there are birds that are not known much, but they play an important role in the ecosystem. One of these birds – the hatchet (Cerorhinca monocerata). Its peculiarity is a massive beak with a horn-shaped outgrowth, thanks to which it got its name.
Hatchets belong to the alcove family (Alcidae)- seabirds that are excellent at diving and foraging underwater. They rarely appear on land and spend most of their lives in the open ocean. Let's take a closer look at their biology, habitat, and interesting features.

1. scientific classification and related species
🔹 Scientific classification:
✔ The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
✔ Type: Chordal (Chordata)
✔ Class: Birds (Aves)
✔ Row: Gray-haired (Charadriiformes)
✔ Family: Alcoves (Alcidae)
✔ Gender: Hatchets (Cerorhinca)
✔ View: Hatchet (Cerorhinca monocerata)
🔹 Related views:
✔ Atlantic Dead End (Fratercula arctica)
✔ Pacific Dead End (Fratercula cirrhata)
✔ Walrus (Alca torda)
Hatchets – the only species of its kindwhich makes them unique among the alcove birds.
2. Appearance and physical characteristics
✔ Body lengthSize: 35-40 cm
✔ WingspanSize: 60-65 cm
✔ WeightWeight : 500-750 g
🔹 Main features of appearance:
✔ Black plumage above and gray or whitish below.
✔ Large triangular beak with a horn-shaped outgrowth, which is especially noticeable during the mating season.
✔ Small dark eyes with a white ring around them.
✔ Short, strong wings, adapted for swimming under water.
Bright yellow or orange feet with swimming webs.
🔹 Interesting features:
The horn growth on the beak appears only in adults and disappears after the breeding season.
✔ In flight, the hatchet quickly flaps its wings, resembling a small penguin.
✔ Its beak has special scallops that help hold several fish at the same time.

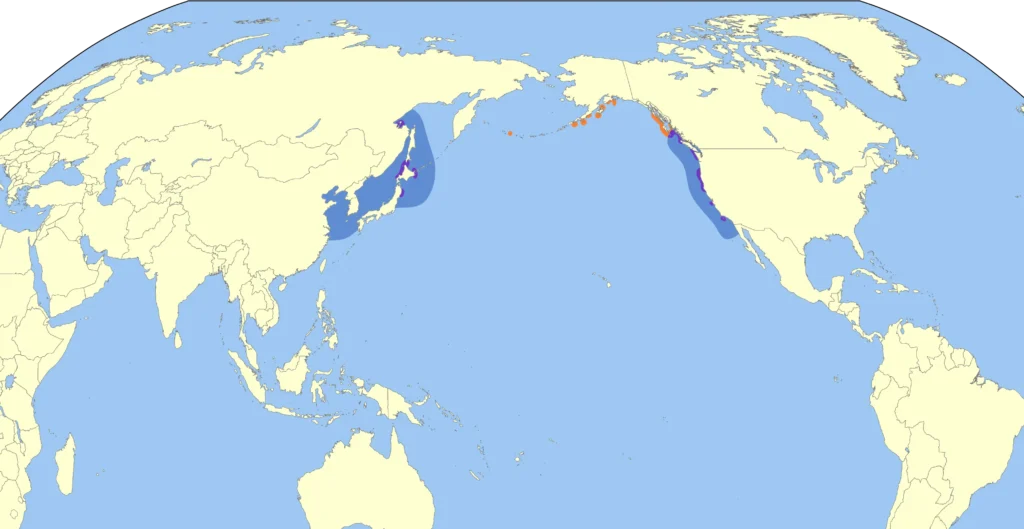
3. Habitat and habitat
🌍 Where do hatchets live?
✔ North Pacific - from Japan and Korea to Alaska and California.
Large colonies populate the Aleutian Islands, the Kuril Islands, Kamchatka and the Bering Sea.
✔ They nest on rocky islands and coasts with dense vegetation.
🔹 Typical nesting sites:
✔ The Aleutian Islands are the largest colonies.
✔ Kuril Islands-zones with a temperate climate and plenty of food.
✔ St. Matthew's Island (Alaska) is one of the most important toporiki nature reserves.
Hatchets they spend most of their lives on the high seasby returning to land only to breed.
4. lifestyle and nutrition
🍽 What do hatchets eat?
✔ Small fish (capelin, herring, anchovies).
✔ Crustaceans (shrimp, crabs).
✔ Squid and other cephalopods.
🔹 How do they hunt?
✔ Dive to the depths up to 50 m.
✔ Use the wings as flippers to move in the water.
✔ Catch fish in several passes, bringing it in the beak to the nest.
🔹 Interesting features:
✔ Hatchets can stay underwater up to 1 minute.
✔ At one time able to catch 5-10 Fish.
5. breeding and raising chicks
✔ Monogamous birdsforming pairs for life.
✔ Nest in burrows or natural gorges.
✔ The female lays only one egg per year.
✔ Incubation continues 40-50 days.
✔ Chicks leave the nest due to 45-50 days after birth.
🔹 Interesting habits:
✔ Parents take turns caring for the egg and feeding the chick.
✔ Chicks leave the nest at night on their own and go to sea.
✔ To strengthen the pair, partners often perform beak-touching rituals.

6. natural enemies and threats
🚨 Natural predators:
✔ Eagles, large gulls, skuas-attack adult birds.
Foxes, arctic foxes and raccoons destroy nests.
🌍 Threats from people:
✔ Ocean pollution from plastic and oil.
✔ Mass fishing that reduces the food resources of birds.
✔ Invasion of nesting islands by invasive predators.
🔹 Population status:
Although the population is declining, hatchets are still common in many regions.
✔ There are more than 3 million individuals.
7. Interesting facts about hatchets
✔ Due to its horn-shaped beak, the hatchet is sometimes referred to as "unicorn of the sea”.
✔ In flight, they can accelerate to 70 km / h.
Most of the year they live in the open sea, relying only on the water as a platform for recreation.
✔ Hatchets have the ability to recognize their offspring even among a large colony.
✔ They use the Earth's magnetic field to navigate during migrations.
Conclusion
Hatchet is a unique representative of seabirds, which combines the grace of a diver and the brightness of a Northern inhabitant. His life is full of difficult challenges, but thanks to adaptations and dedication to his family, this mysterious bird continues to reign supreme in the cold waters of the Northern Ocean. 🐦🌊