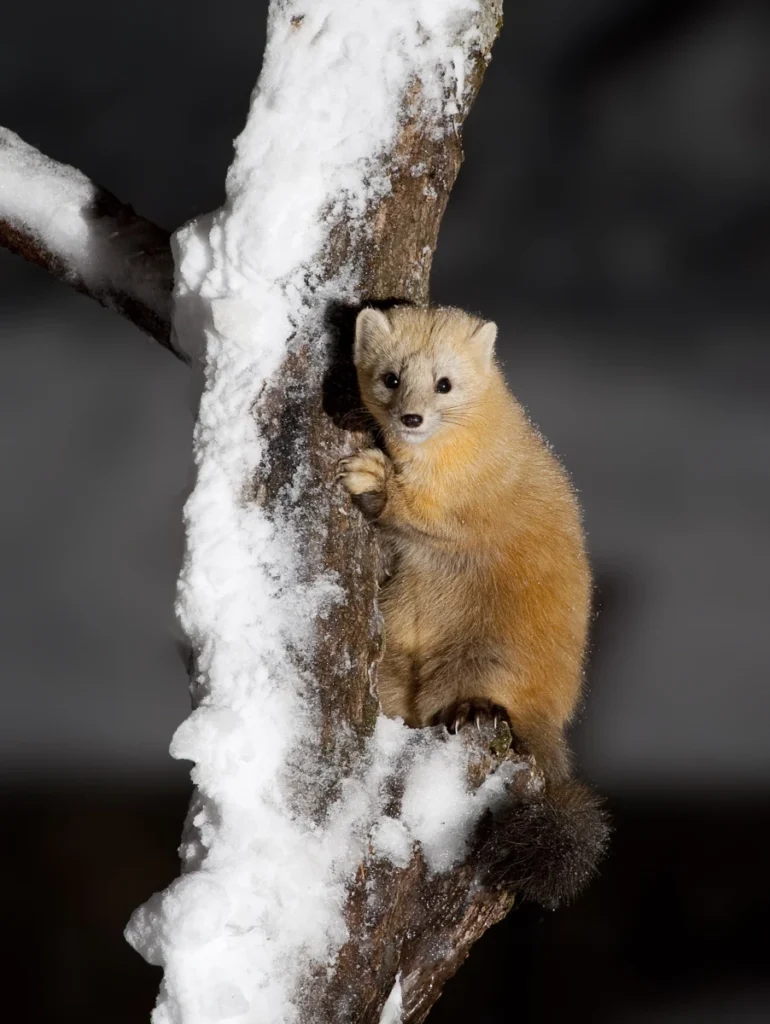
Sable (Martes zibellina) is a small carnivorous mammal from the marten family (Mustelidae), which is a symbol of the Siberian taiga. It is known for its extremely thick and soft fur, which has long been considered one of the most expensive in the world. Sables are skilled hunters, agile climbers, and important elements of the ecosystem of North Asian forests.
These animals lead a solitary lifestyle, are territorial, and have a keen sense of smell that helps them hunt small animals. They have perfectly adapted to living in the harsh conditions of the taiga, where temperatures can drop below -40°C.

Classification and scientific name
• The Kingdom: Animals (Animalia)
• Type: Chordal (Chordata)
• Class: Mammals (Mammalia)
• Row: Predatory animals (Carnivora)
• Family: Martens (Mustelidae)
• Gender: Martens (Tuesdays)
• View: Sable (Martes zibellina)
Sable is a close relative of the forest marten (Tuesday Tuesday) and American marten (Martes americana), but has thicker fur and is better adapted to harsh climates.
Appearance
Dimensions and weight
📌 Body length: 35-55 cm
📌 Tail length: 12-20 cm
📌 Weight: 0.8-1.8 kg (sometimes up to 2.2 kg)
Color and fur
✔ The color of the coat: varies from light yellow to dark brown
✔ Chairman: slightly lighter than the body, sometimes with reddish tints
✔ Breasts: may have a light or yellow spot
✔ Fur: very thick, silky, with a high level of thermal insulation
One of the characteristic features of sable is his fluffy tailwhich is used for balance while moving through the trees and helps to keep warm in winter.
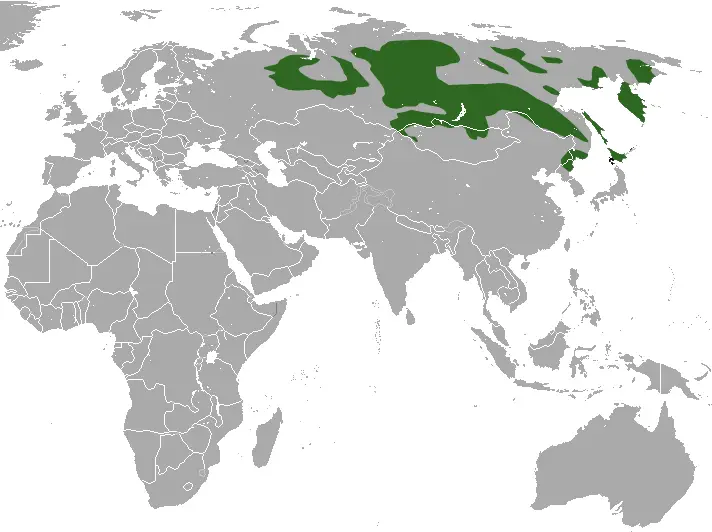
Range and habitat
🟢 Spread
The sable lives mainly in Asia:
• Russia: Siberia, the Far East, the Urals
• Mongolia
• China (northern regions)
• Japan (Hokkaido)
• Korea
In the past, sable was also found in Europe, but due to intensive hunting, its population has declined.
🟢 Living environment
✔ Taiga: primary habitat, especially cedar and coniferous forests
✔ Mountain forests: up to 2000 m above sea level
✔ Mixed forests: with dense undergrowth
Sable does not like open spaces and avoids steppes and tundra.
Lifestyle and behavior
🌟 Solitary predator
Sable leads territorial way of lifemarking its territory with scent marks. Within its territory, it actively moves in search of food.
🌟 Activity time
✅ Mostly a nocturnal hunter
✅ In winter, it can be active during the day
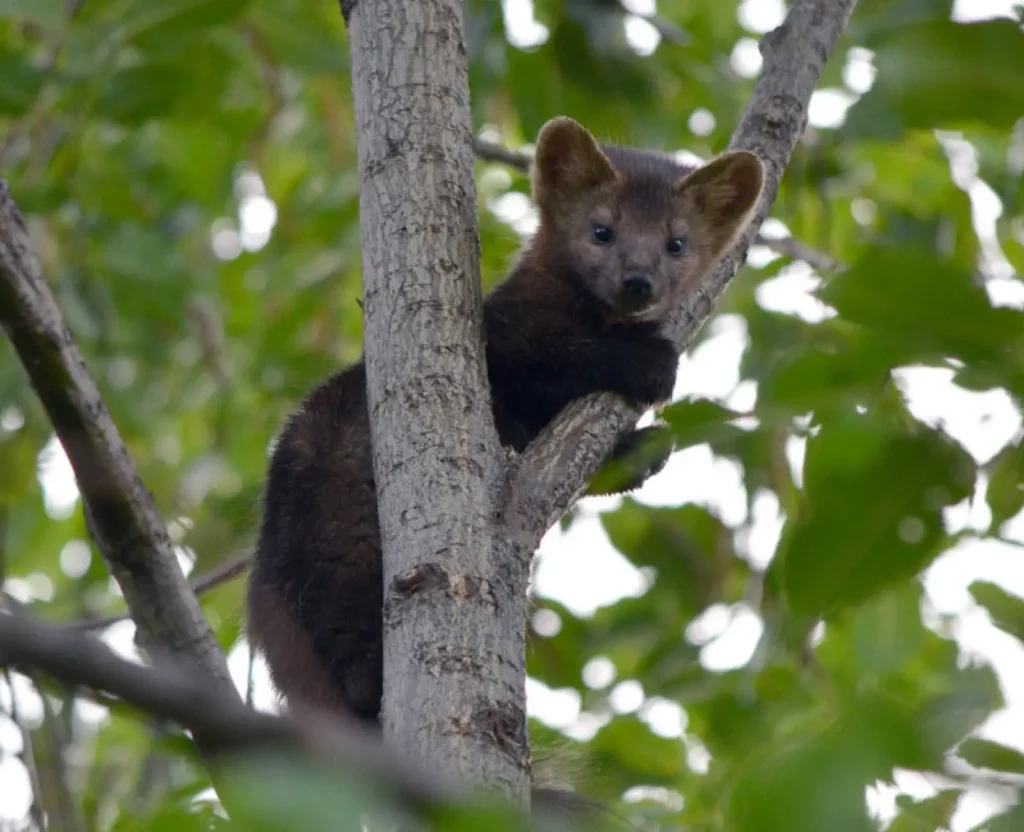

🌟 Behavioral characteristics
✔ Excellent cragsmanbut hunts mostly on the ground
✔ In case of danger can climb a tree or hide in a hole
✔ Does not go into hibernationbut on cold days it can stay in hiding for a long time
Nutrition and hunting skills
🍖 Omnivorous predator with preferences
Sable universal hunterthat adapts to the food available.
✅ Basic diet:
✔ Small rodents (mice, squirrels, pika)
✔ Birds and their eggs
Insects, fish, frogs
✔ Distance
Nuts, berries, fruits
In the fall, sables actively eat pine nutswhich allows them to accumulate fat reserves for the winter.
💡 Hunting tactics
- The sense of smell is the main tool for finding prey.
- It can chase a victim, jump on them from above, or grab them in an ambush.
- In winter, it uses tunnels under the snow to get to rodents.
Reproduction and life cycle
❤️ Mating season: June-August
❤️ Pregnancy: 250-300 days (due to the slow development of embryos)
❤️ Number of children: 2-5 (sometimes up to 7)
❤️ Puberty: 2 years
👶 Babies are born blind, covered with thin fluff.
👩👧 The mother feeds them with milk for up to 2 months.
🏠 They spend the first 3 months of their lives in a burrow.
Sables can live up to 10 years in the wild and to 18 years in captivity.
Natural enemies and threats
🔴 Birds of prey and animals
✔ Wolves
✔ Foxes
✔ Eagles and owls
🔴 Threats from humans
✔ Mass hunting for fur
✔ Deforestation and habitat destruction
Sable and fur industry
🐾 The value of fur
Sable fur has extraordinary softness, silkiness and thickness, making it one of the most expensive in the world.
📌 The main centers of fur trade:
✔ Russia (Irkutsk, Krasnoyarsk)
✔ Canada
✔ China
Due to overhunting in the 20th century, the number of sables plummeted. Today, there are restrictions on the capture of wild sable, and its breeding on fur farms is developing.
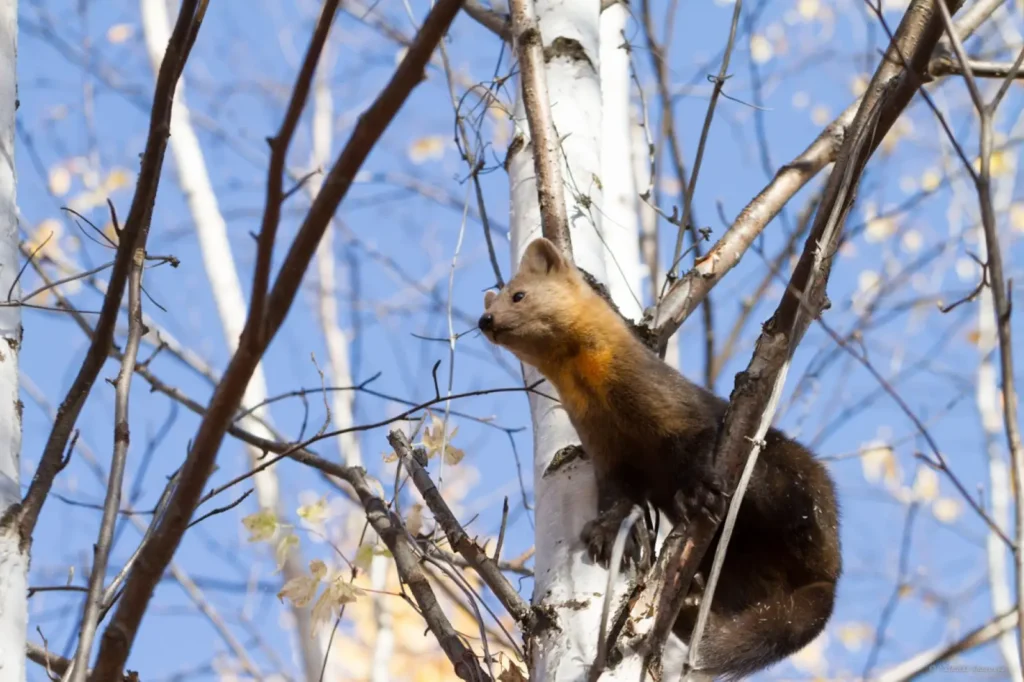

Protection status and protection measures
🟢 Status in nature:
🔹 Not endangeredbut requires control of numbers.
🔹 Listed in the IUCN Red List as a species in need of hunting regulation.
🟢 Security measures:
✔ Control of wild sable catch
✔ Creation of nature reserves
✔ Development of farm breeding
Conclusion
Sable is a unique representative of the taigaThe musk ox is an animal that combines predatory agility, intelligence, and beauty. Its fur is considered to be one of the most valuable in the world, but the preservation of the species depends on the responsible attitude of humans to nature.
